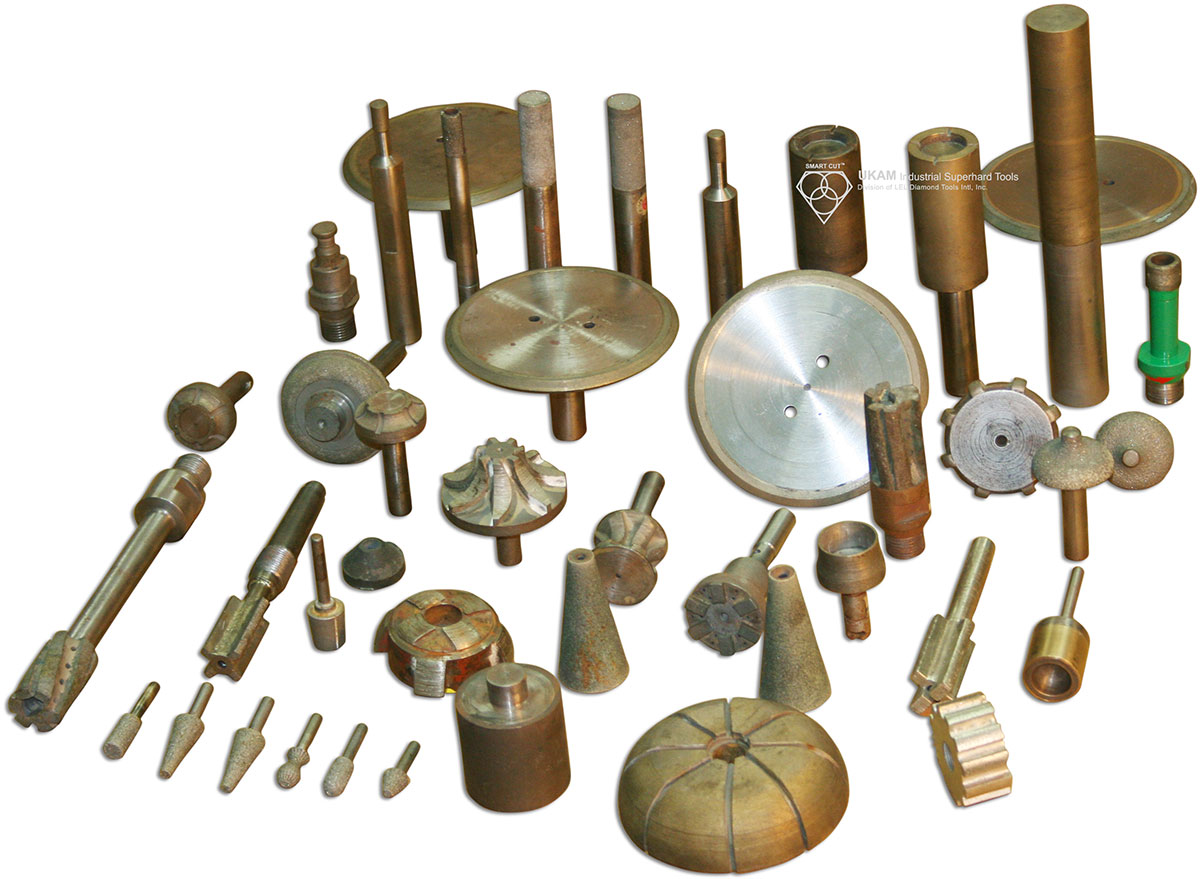
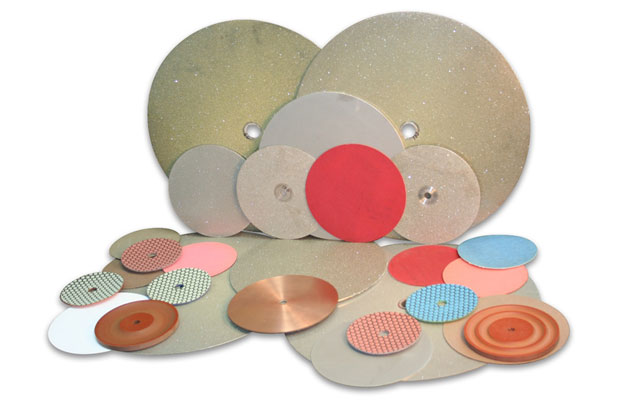
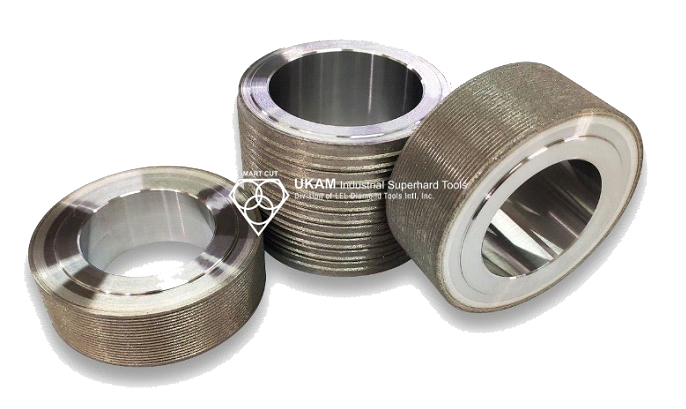
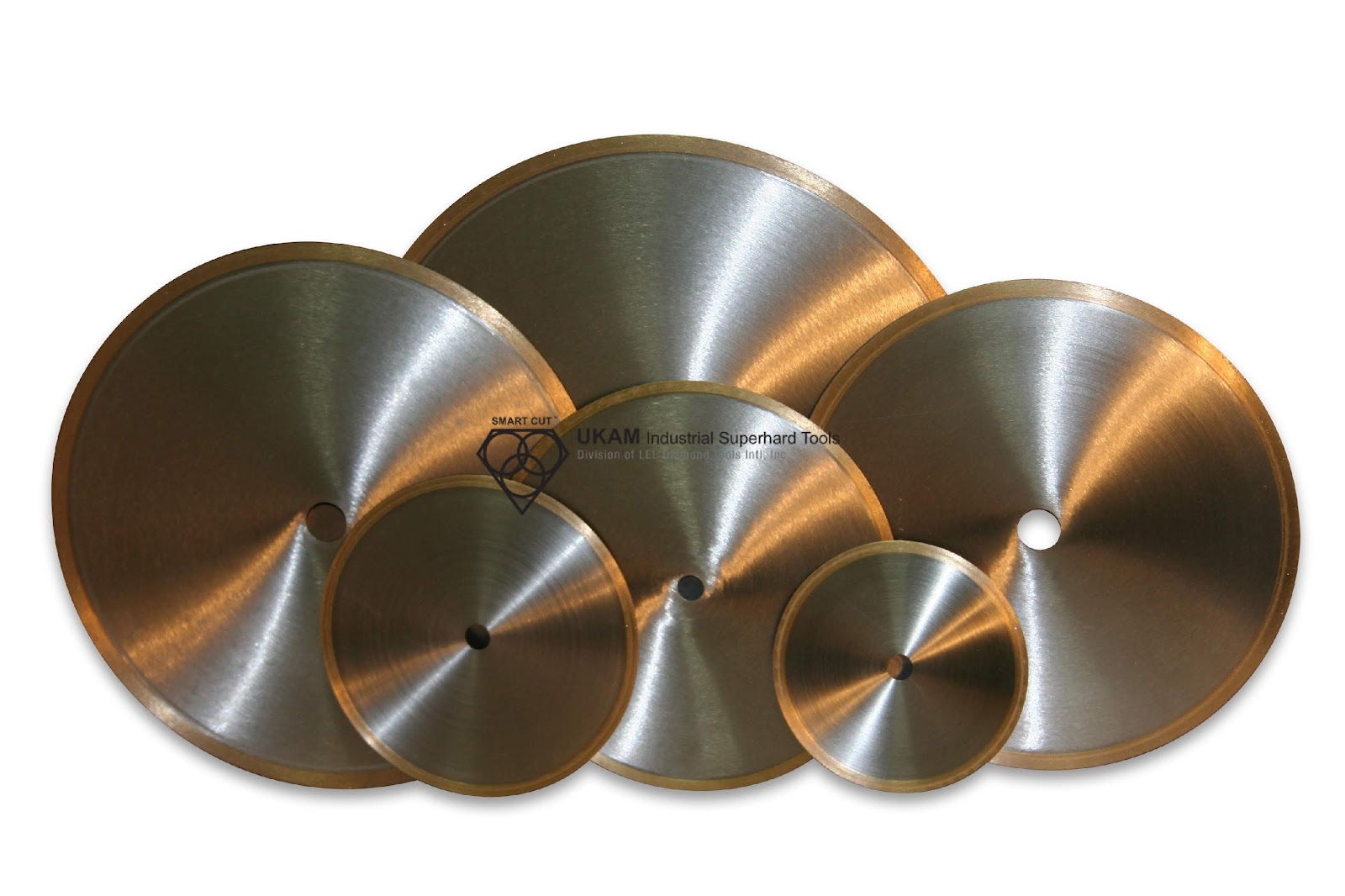
Learn everything you wanted to know about resin bond diamond tools. How they are made, what types are available and their application
Everything you wanted to find out about Resin Bond Tools
How they are Made & Their Application
Learn everything you wanted to know about resin bond diamond tools. How they are made, what types are available and their application
Resin Bond is an organic bond matrix that is formed by high pressure and high temperature. Phenolic resin is used as the bonding agent in majority of resin bond diamond tools. This bond is typically cured at temperatures of 150 to 200 degrees Celsius. Resin Bond is the softest of all the bonds, frequently used in applications that require a smooth surface. This type bond system that is used on majority of grinding applications on large variety of materials. Resin Bond Diamond Matrix promotes faster bond wear, allowing for diamond particles/crystals to break out of their matrix faster, so that new sharp diamond particles become exposed.
ADVANTAGES:
-
 Unmatched Cut Quality (eliminates secondary finishing operations)
Unmatched Cut Quality (eliminates secondary finishing operations)
-
 Faster & Freer Speed
Faster & Freer Speed
-
 Less Heat Generation than other bond types
Less Heat Generation than other bond types
-
 Less Stress to material than other bond types
Less Stress to material than other bond types
-
 Will work the hardest material (even natural diamond)
Will work the hardest material (even natural diamond)
-
 Can be used dry (without coolant) when needed
Can be used dry (without coolant) when needed
-
 Can withstand Higher Temperature than sintered (metal bond) tools
Can withstand Higher Temperature than sintered (metal bond) tools
-
 Perfect for fragile and delicate materials
Perfect for fragile and delicate materials
-
 Minimize Chipping, Improve Surface Finish, Minimize Material Deformation
Minimize Chipping, Improve Surface Finish, Minimize Material Deformation
BENEFITS:
-
 Increase Tool Life
Increase Tool Life
-
 Reduce Chipping
Reduce Chipping
-
 Reduce Tool Wear
Reduce Tool Wear
-
 Increase Process Consistency
Increase Process Consistency
-
 Maintain Consistent Cutting Speed
Maintain Consistent Cutting Speed
-
 Reduce Blade Change & Mounting Cost
Reduce Blade Change & Mounting Cost
-
 Reduce Cost
Reduce Cost
ADVANTAGES:
-
 maximum cutting performance
maximum cutting performance
-
 no glazing
no glazing
-
 faster cutting action
faster cutting action
-
 improved surface finish qualityy
improved surface finish qualityy
-
 better coolant retention
better coolant retention
-
 No Material Deformation
No Material Deformation
-
 No Contamination
No Contamination
-
 Longer Life than any other Resin Bond Tools in Industry
Longer Life than any other Resin Bond Tools in Industry
-
 Self-sharpening matrix
Self-sharpening matrix
-
 Superior cut quality
Superior cut quality
-
 The widest variety of bond matrixes
The widest variety of bond matrixes
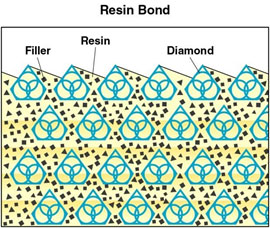
This self sharpening characteristic of resin bond matrix, based on faster bond wear is what make this blade an excellent choice for large variety of hard and brittle materials. Primary advantage of this bond type is Minimizing Chipping, and in majority cases elimination of secondary finishing operation (grinding/polishing or fire polishing).
Recommended for applications where cut quality and surface finish is very important. Compared to their sintered (metal bond) counterparts. Resin Bond Diamond & CBN offer far superior surface finish than any other bond type.
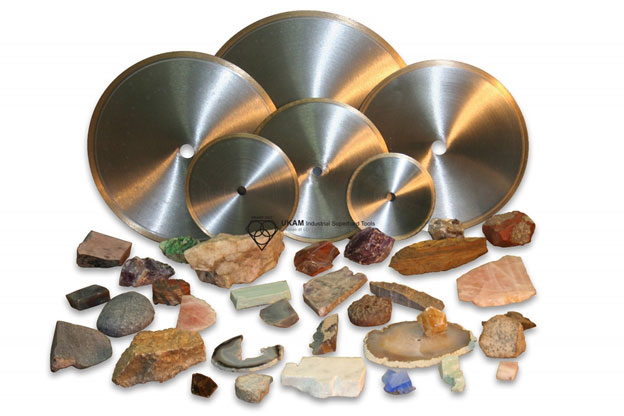
Application Range: cutting, grinding and polishing hard, brittle or delicate materials and where low heat generation or improved surface finish is desired. CBN, Resin bond Tools are recommended for cutting and grinding hard steels above Rc 60 at high speeds.
Example of Applications Resin Bond Diamond Tools are Used:
-
 ceramics
ceramics
-
 glass tubing
glass tubing
-
 optical glass
optical glass
-
 carbides
carbides
-
 composites
composites
-
 semiconductor materials
semiconductor materials
-
 magnetic materials
magnetic materials
-
 exotic metals
exotic metals
Best Cut Quality & Surface Finish
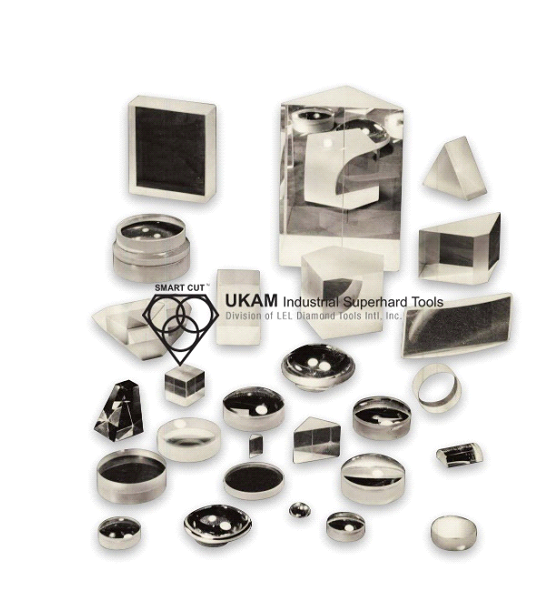
Recommended for applications where cut quality and surface finish is very important. Compared to their sintered (metal bond) counterparts. Resin Bond Diamond & CBN offer far superior surface finish than any other bond type. Recommended cutting, grinding and polishing hard, brittle or delicate materials including ceramics, glass tubing, optical glass, carbides, composites and exotic metals where low heat generation or improved surface finish is desired. Must be used at higher speeds. CBN, Resin bond Tools are recommended for cutting and grinding hard steels above Rc 60 at high speeds.

Its hardness, wear, heat resistance, diamond crystal retention and lubrication is controlled by use of various fillers organic and inorganic (usually ceramic or other metallic powders). Resin bond is low on Youn's modulus, this gives it the free cutting characteristics for which this bond family is known. These properties is what gives this bond the fast cutting speeds, superior surface finish, and minimal chipping. Resin bond diamond tools are used at higher speeds, the most other bond families. Resin bond diamond tools have shorter wheel life because the bond is much softer and brittle, and hence is not able to hold the diamond crystals in place as strong as its sintered (metal bond) counterpart.
Diamond Type Used for Resin Bond Diamond Tools
The diamond and CBN crystals used for resin bond wheels are different from those used for metal bond as well. Diamond Crystals used for resin bond are frequently polycrystalline, low strength, metal clad diamond crystal. They are irregular-shaped and easy to micro fracture. This creates new cutting edges constantly while cutting, giving the self sharpening characteristic for which resin bond is known. Often metal coated and unevenly shaped diamond crystal is preferred in manufacture of this bond type as it helps further improve crystal retention. Resin Bond Diamond Tools are typically used with coolant, but can also be used dry on many applications. By adding specializes filler and/or using specialized coated diamond crystal to reduce heat generation.
Resin Bond Diamond Tools Composition
majority of resin bond diamond tools are based on either phenolic resins or thermally table phenol aralky resins. They are used in form of very fine powder which accounts from around 30 to 40 wt % of the bond in dry and wet diamond wheels. To impart strength to the bond, the resins are mixed with alumina oxide of silicon carbide filler. Various oxide base drying agents, graphite or polytetrafuoor-ethlene lubricants, as well as aluminum, copper or silver powders are also added in small amounts in order to reduce and dissipate the frictional heat generated in cutting.
Example of Fillers Used for Resin Bond Diamond Tools:
Alumina Oxide
Silicon Carbide
Silicon Carbide
Silicon Carbide




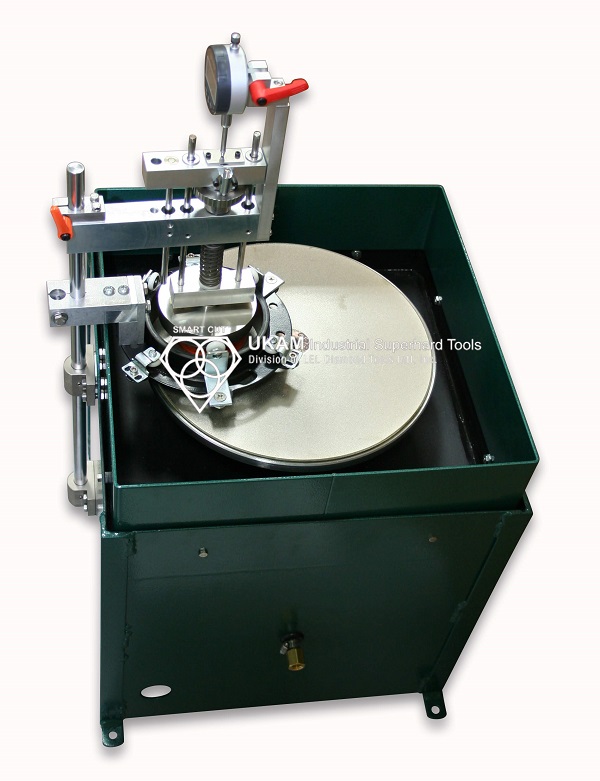
How Resin Bond Diamond Tools are Manufactured

Example of Hydraulic Heated Press Used for Production of Resin Bond Diamond ToolsAllows high degree of control of pressure, temperature, & time
Compression Molding process is used in manufacture of high precision tools
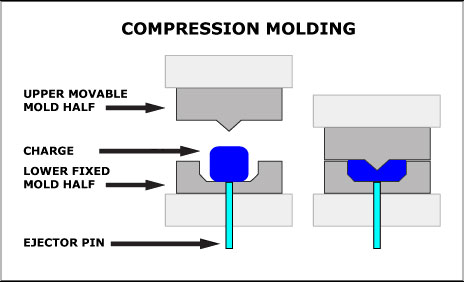

Resin Bond Diamond Tools Manufacturing Variables:
-
 Diamond Type Used
Diamond Type Used
-
 Diamond Concentration
Diamond Concentration
-
 Pressure Used
Pressure Used
-
 Temperature Used
Temperature Used
-
 Curing Cycle Time
Curing Cycle Time
-
 Fillers Used
Fillers Used
-
 Bond Formula (proportion of components)
Bond Formula (proportion of components)
What We Offer & How We Are Different
UKAM Industrial Resin Bond Diamond & CBN diamond tools are manufactured with advanced molding process. Available in a large variety of geometries, diamond sizes, diamond concentrations, and bond harnesses. We can hold very high precision tolerances on tool diameter, thickness, and grind almost any form or radius. We can produce resin bond diamond tools/wheels as small as 2mm (.080") to 609mm (24") Diameter. Thickness from as thin as 0.10mm (.004") to 101mm (4"). Diamond & CBN Grit sizes from as coarse as 60 mesh to 3 micron. Tolerances on Thickness starting 5 microns and up. Number of popular specification resin bond tools are kept in stock as part of our stock program. We can also produce almost any specification within fairly short lead time. Contact us for Free Quote & Application Evaluation Today!