Selecting the right parameters for your Precision & Ultra Thin Diamond Blade can be a very time consuming, trial & error frustrating process. The guide below has been designed to help you better understand the most important diamond blade variables, which will play a major role in performance, cutting speed, and surface finish of your Precision Diamond Blade.

Selecting the right parameters for your Precision & Ultra Thin Diamond Blade can be a very time consuming, trial & error frustrating process. The guide below has been designed to help you better understand the most important diamond blade variables, which will play a major role in performance, cutting speed, and surface finish of your Precision Diamond Blade.
Selecting the Right Diamond Blade for your specific Material / Application will also minimize the secondary operations that may be required afterwards such as lapping, grinding, & polishing. The following are some factors to consider when selecting the right diamond blade for your application.
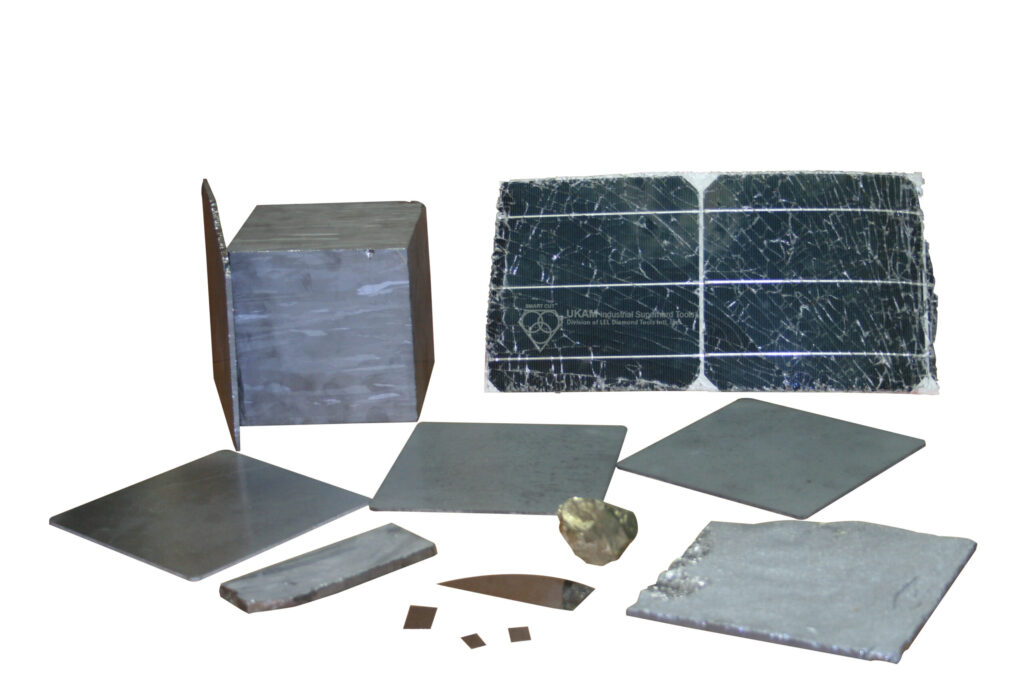
The ever increasing variety of ultra hard, new generation, composite, engineered, highly metallic content and exotic materials, transform the way we look at Diamond Blades for Slicing, Dicing, Wafering, Cut-off, Singulation, Grooving, Slotting, Cross Sectioning, Gang Sawing, Slabbing, Rough Cutting applications. And set many age old conventional diamond blade technologies, equipment and diamond cutting methods obsolete. New materials require different diamond blades & technology.
MATERIAL TO BE CUT
Materials you are planning to cut will have a large impact in the types of diamond blades you can use. If you are cutting hard alumina or sapphire, it is generally recommended that you use a soft bond, thin kerf diamond blades. However, if you are cutting abrasive materials such as sandstone or flagstone, a hard bond, thicker diamond blades may be a better solution.


Advanced Ceramics

Glass & Quarts

Precision Optics

Semiconductor & Photovoltaic

Microelectronics

Ferrous & Non Ferrous Metals

Semi Precious Stone / Lapidary

Natural Stone

Concrete & Construction
Hardness of Material
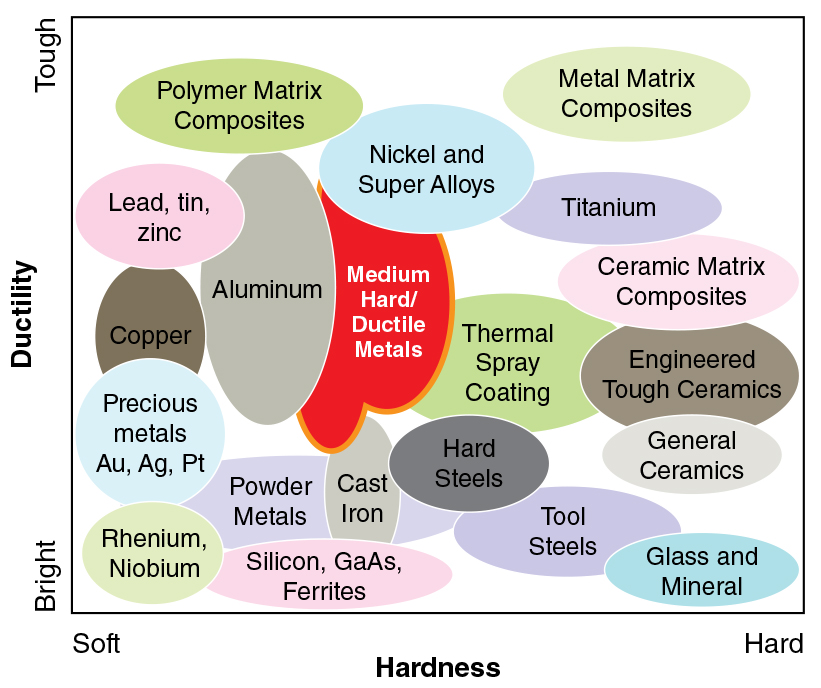
harder materials such as sapphire and alumina will require a softer Diamond Blade Bond. As a rule of thumb harder materials require softer bond, to cut faster and freer. While softer and abrasive materials require a harder bond, to last longer. Material Hardness is defined as the materials capability to resist deformation. All materials are classified by their scale of hardness. Material hardness is measured by many different hardness scales such as Mohs, Vickers, Knoop and other scales of hardness. Further information on determining and understanding hardness of your material is available in this article below.
Material Cost
if the material you are cutting is precious, valuable, or expensive. The diamond blade cost will play a minor role in your cutting operation. It is suggested that you obtain a thin kerf diamond blade to minimize material loss and chipping. It’s always a good idea to have some type of an estimate of target cost and quality per cut.
Material Thickness
the thicker the material you are planning to cut, the greater amount of coolant and water pressure is required.

Material Geometry & Density
Each material has different density, hardness, composition. For this reason a diamond blades and technological processes that may work on one material/application, may not work on another. To obtain optimum results, each diamond blade should be ideally made to factor in the unique differences and properties of each material. Shape, Size, Diameter, Hardness, and Brittleness of your material. These variables will not only affect our diamond blade selection, but your choice material holding / fixturing methods, cutting equipment, speeds & feeds you can use.
EQUIPMENT TO BE USED
The equipment you will be using and its physical condition, will dictate the speeds (RPM’s) and coolants you can use along with your diamond blades. The precision, accuracy, & repeatability of your equipment will also determine the tolerances you will be able to obtain. Somewhat limiting your diamond blade selection. Diamond Blades are usually used on the following equipment:
Precision Diamond Sawing Equipment
a.) Tile Saw
d.) Surface Grinder
e.) Dicing Saw
g.) Precision Gang Saws
h.) Industrial & Laboratory Diamond Band Saw
e.) Other Equipment

An adequate diamond cutting saw for diamond blade use must provide:
- Adequate power
- proper RPM
- A rigid, true running spindle with good bearings
- Proper alignment after blade is mounted between its flanges
- Flanges that are flat and parallel equal to at least 1/3 of the blade diameter in size
- work table that feeds smoothly and without side play
Most Precision & Ultra Thin Diamond Blades are used on computer/cnc controlled precision cutting equipment. Equipment used by Manufacturing and Research & Development facilities is usually different. Precision Diamond Sawing equipment used by Manufacturing facilities world wide varies with industry used in, material dimensions, & materials machined. Semiconductor manufactures (chip makers) favoring dicing saws that are equipped with high speed air spindles capable of reaching up to 35,000 RPM. Precision Gang saws are used in high production scenarios of semiconductor packages (singulation), slicing of ultra hard & brittle materials, optics, as well as glass & quartz tubing, rods and many other materials. Smaller ultra hard, brittle material, and optics manufacturing operations use surface grinders for slicing, grooving, & slotting large variety of materials.
COMMON PRECISION DIAMOND SAWING OPERATIONS FOR INDUSTRY AND R & D
Diamond Slicing
Sawing. Machining operation in which a powered machine, equipped with a blade having milled or ground teeth, is used to part a material (cut-off) or give it a new shape (contour band sawing, band machining). Four basic types of sawing operations are:
Circular or annular (I.D.) sawing
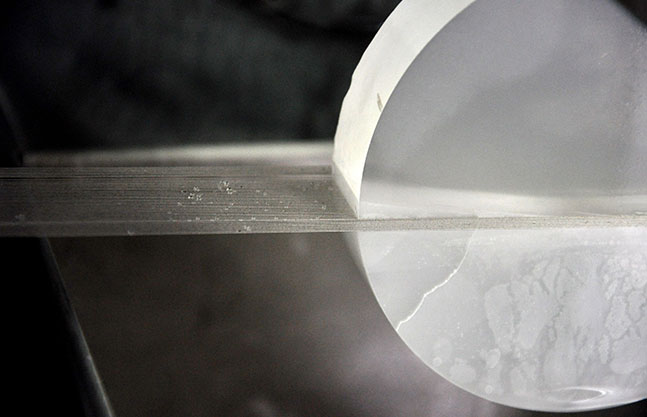
This process utilizes a rotating circular, toothed blade to cut off the material much as a workshop table or radial saw cuts wood. The ring shaped blade operates under high tension and is held by a precision chick. The cuts made with this method are precise wit little material loss and a good surface finish.
Dicing
Dicing (or diamond-wheel sawing) is used in the micro-electronics industry for fine, accurate, partial and cut-through of exotic, very hard and brittle materials into small squares, or die. Diamond wheel dicing is the most common technique in the industry because of the superior cut quality. It is possible to keep the cut width, depth, straightness, and edge quality within tight tolerances.

Sectioning / Wafering
The first stage of sample preparation, metallography, and failure analysis process. A failed part or piece of material is cut off to be studies and observed in order to identify the origin and reason of part/material failure. The main objective is to cause as minimum material deformation to sample as possible and not alter material structure while cutting. Another important consideration is to minimize additional steps required for sample preparation process. Depending on the type of failure, it may be necessary to take several specimens from the area of failure and from adjacent areas.
Gang Sawing
A principal advantage of gang saws is realized when cutting very hard materials. When extremely slow feed rates are necessary, an entire substrate can be cut in just one or two passes with a gang saw. Thus, high-speed production is feasible, and extreme accuracy can be realized. For sawing applications, gang arbors are available to very precise tolerances, maintaining slot widths within ±0.0002 in ( ±5.08 mm), with a gang pitch tolerance of 0.0002 in, non-cumulative.

The best solution for advanced material and non ferrous material high volume production operations. Unlike wafer dicing saws that were designed for more thinner substrate materials. The capabilities of a diamond gang saw are almost limitless. Gang saws have been proven to provide high production volume at minimum cost.
Multi-Blade cutting system makes all cuts simultaneously and automatically separates end cuts from finished pieces. Gang saws are capable of cutting tubes, rods, and flat glass, quartz, carbon, ceramics, plastics, fiber glass, hybrid and exotic materials and most metals. Normal length tolerance is +/- .002". Squareness is +/- 1.0 degrees. Offering Speed, Precision, & Cost Savings. Designed for machining materials such as Glass, Quartz, Ceramics, and Metals. Cut 10 times faster over conventional sawing methods. Gang saws can cut 400 to 6,000 parts per minute 40/1000 to 59 parts in length, Precision Tolerances + 1/200.

Diamond Band Sawing
This process utilizes a flexible, toothed blade is welded into an endless band that rides on wheels driven by two pulleys and is guided through the work cut off or contour. A band saw’s blade is diamond coated by electroplating, a process in which an electrical current deposits the coating onto the blade.
This produces a hard, brittle Ni matrix that holds the diamonds in place and permits precise cutting on a variety of materials. A friction saw is a special band saw capable of achieving band velocities of up to 15,000 sfpm or more. Material removal is accomplished in two steps: frictional heat softens the substrate, and the teeth scoop out the molten material. Carbon steel bands are used for flexibility to obtain maximum band life. Method is excellent for cutting extremely hard substrates.
Diamond Grinding
Machining operation in which material is removed from the workpiece by means of abrasive points mounted in a matrix in the form of a wheel, stone, belt, paste, compound, or similar application vehicle. Takes various forms: precision surface grinding (creates flat and squared surfaces); cylindrical grinding (process that creates external cylindrical and tapered shapes, fillets, undercuts, etc.); centerless grinding; chamfering; thread and form grinding; tool and cutter grinding; offhand grinding; lapping and polishing (grinding steps using extremely fine grit to create ultra-smooth surfaces); honing; and disc grinding. Grinding steps take several forms: internal, external, and plunge grinding.
Usage Volume
Your diamond blade requirements will greatly vary with your frequency of use and the number of cuts you need to make. Diamond Blades are generally used for:
INDUSTRY / PRODUCTION

Ultra Thin & High Precision Diamond Blades are used everyday in thousands industries & operations to manufacture products that play an important role in our everyday lives. Typical Manufacturing Operations used diamond blades for Slicing, Dicing, Wafering, Cut-off, Singulation, Grooving, Slotting, Gang Sawing, Slabbing, Rough Cutting. On a full variety of advanced, non-ferrous and ferrous materials, ultra hard materials, precision optics, semiconductors and electronic components, which can be found in: PCs, cellular phones, DVD players, digital cameras, home video game systems etc. that play an important role in our modern every day lives. Diamond Blade & technical requirements are diverse as the manufacturing operations that use them. Typically manufacturing engineers, technicians & machinists demand a high level of consistency, accuracy, yield (output per cost), increased production rates, surface finish quality, & reduced material loss.
What is common about these applications is the Diamond Blade will be used every day or several times a day, cutting several thousand parts or until the blade is warn out and replaced.

Metal Bond (Sintered) diamond blades are usually recommended for this type of heavy duty use. However, if you have a very fine or specific finish requirement and do not polish material after cutting. HYBRID Bond diamond blades may be the best solution for your application. UKAM Industrial Superhard Tools has the Experience & Solutions to help you resolve even the most complex manufacturing challenges. Discover why thousands of advanced, ultra hard and brittle material, optics, semiconductor, composite, glass, stone, & jewelry manufacturing facilities around the world turn to UKAM Industrial Superhard Tools to optimize their diamond sawing & machining operation to ultimate level of efficiency.
RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT / SAMPLE PREPARATION
Diamond Blade requirements in Research are diverse as fields and researchers that used them. Most researchers & application engineers are primarily concerned about preserving material true micro structure and introducing least amount of damage & deformation possible to material / sample being worked on.
Research Applications range from materials sciences, metallogrpahy, advanced materials, advanced/technical ceramics, optics, sample preparation, composites to new and breakthrough fields such as MEMS, Biotechnology and Nano Technology. Typical Research diamond blade users include Universities, Government or Commercial Laboratories,
Military Research Facilities, Space & Science Organizations, as well as R & D departments of large organizations. Today, most laboratories and R & D facilities , work with dozens of materials.
Frequently each material requires a different sectioning method and sample preparation approach. Selecting the right equipment, consumables, and parameters for your specific material/application will significantly affect your sectioning operation.
UKAM Industrial Superhard Tools understands the challenges faced by faced by R & D Organizations and has developed diamond blades, equipment, accessories, and TOTAL SOLUTIONS to address most common R & D applications. We are constantly engaged in R & D and process development ourselves to keep up with increasing demands of the complex / advanced material world / community.
Technical Requirements/Specifications

Chipping/Finish Requirements
if you have an application where surface finish and chipping is a critical factor, a sintered (metal bond) diamond blades with a very fine diamond grit may be the best solution. Resin bond and HYBRID Bond diamond blades are usually another option
Tolerances
if you are using diamond blades for slotting or grooving or your material/product requires specific tolerances, you will need a custom diamond blade specifically designed for your application.
Material Cost
if the material you are cutting cut precious, valuable, or expensive. The diamond blade cost will play a minor role in your cutting operation. It is suggested that you obtain a thin kerf diamond blade to minimize material loss and deformation. It’s always a good idea to have some type of an estimate of target cost and quality per cut.
d) cutting speed -
COOLANT TO BE USED

Your capability to use coolant while cutting, will seriously effect your diamond blade selection. Most precision & ultra thin diamond blades in precision diamond sawing operations must be used with coolant. Shorter cutting life, material and cut deformation will result when using blades dry. Electroplated (nickel bonded) diamond blades with coarse mesh size of diamond, braised bond cutting blades and some Resin Bond Blades may be used dry (without water) depending on the application (material being cut). UKAM Industrial Superhard Tools does have the capability to manufactured diamond blades to be used without coolant. However, using diamond blades dry is not recommended on most applications. When chance prevails, use all diamond blades with coolant.
Find more information about using coolant>>>
DIAMOND & CBN ABRASIVE SELECTION
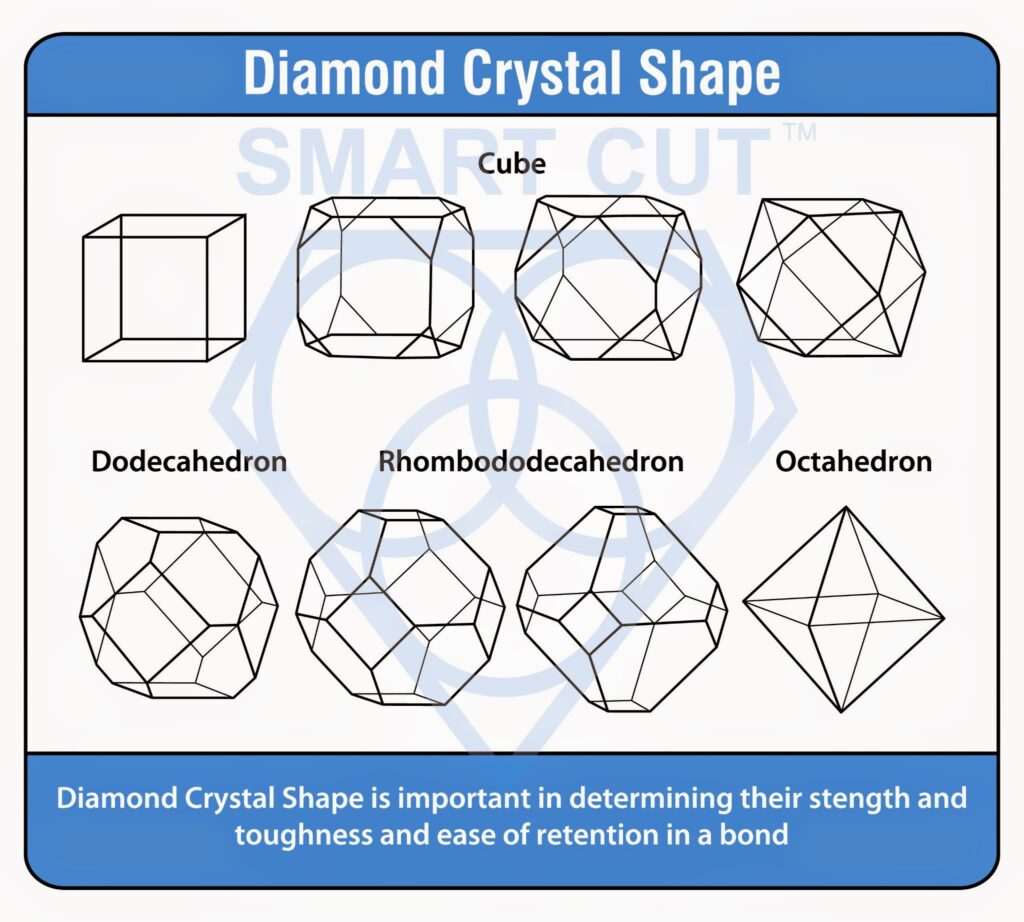
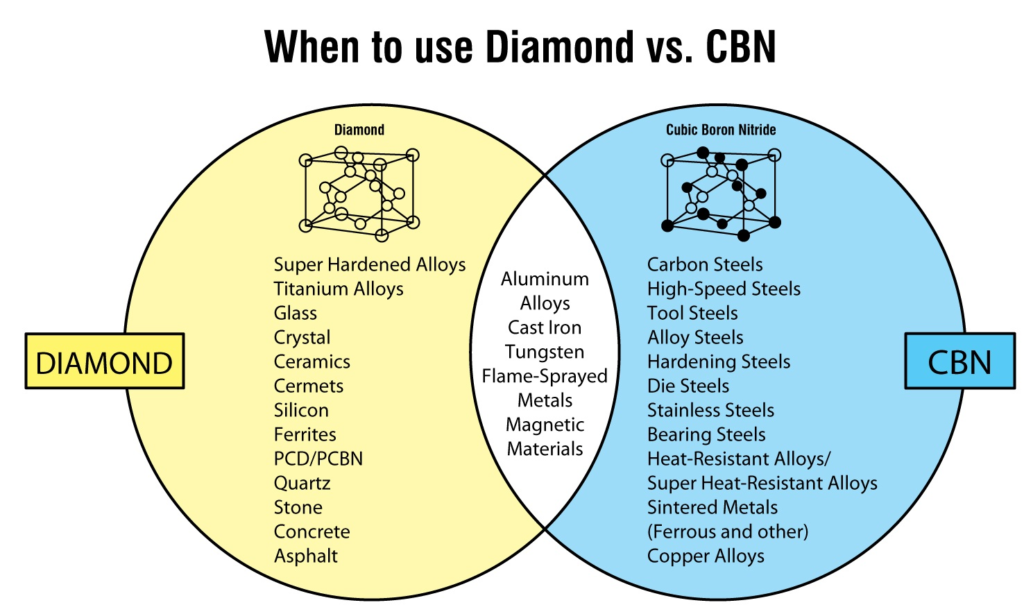
Diamond is universally recognized as the hardest substance known to man. Diamond is recommended for machining hard & brittle materials, optics, semiconductor packages, advanced materials, composites, ferrous & non ferrous metallic materials from 40 on Rockwell scale and up. Diamond crystals can be synthetically grown in a wide variety of qualities, shapes and sizes. Diamond is grown with smooth crystal faces in a cubo-octahedral shape and the color is typically from light yellow to medium yellow-green. Diamond is also grown to a specific toughness, which generally increases as the crystal size decreases.

Synthetic (Man Made) Diamonds - Most frequently used for most diamond blade manufacturing including sintered (metal bond), resin bond, electroplating (nickel bond). Synthetic diamond is more consistent in particle shape, hardness, and density. Synthetic diamond has replaced natural diamond in most applications because of this ability to tailor-make the diamond for the specific application.
Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) - often used for machining materials with high metallic content.
Materials recommended for cutting with CBN:
-
 Alloy steels (45-68 RC)
Alloy steels (45-68 RC)
-
 Carbon tool steels (45-68 RC)
Carbon tool steels (45-68 RC)
-
 Die steel (45-68 RC)
Die steel (45-68 RC)
-
 High speed steel (45-68 RC)
High speed steel (45-68 RC)
-
 Chilled cast iron
Chilled cast iron
-
 Ni Hard
Ni Hard
-
 Forged steel
Forged steel
-
 Meehanite iron
Meehanite iron
-
 Moly chrome steel rolls
Moly chrome steel rolls
-
 Inconel 600
Inconel 600
-
 Rene
Rene
-
 Monel
Monel
-
 Stellite
Stellite
-
 Colmonoy
Colmonoy
-
 Waspoloy
Waspoloy

Find more information about CBN (cubic boron nitride)>>>
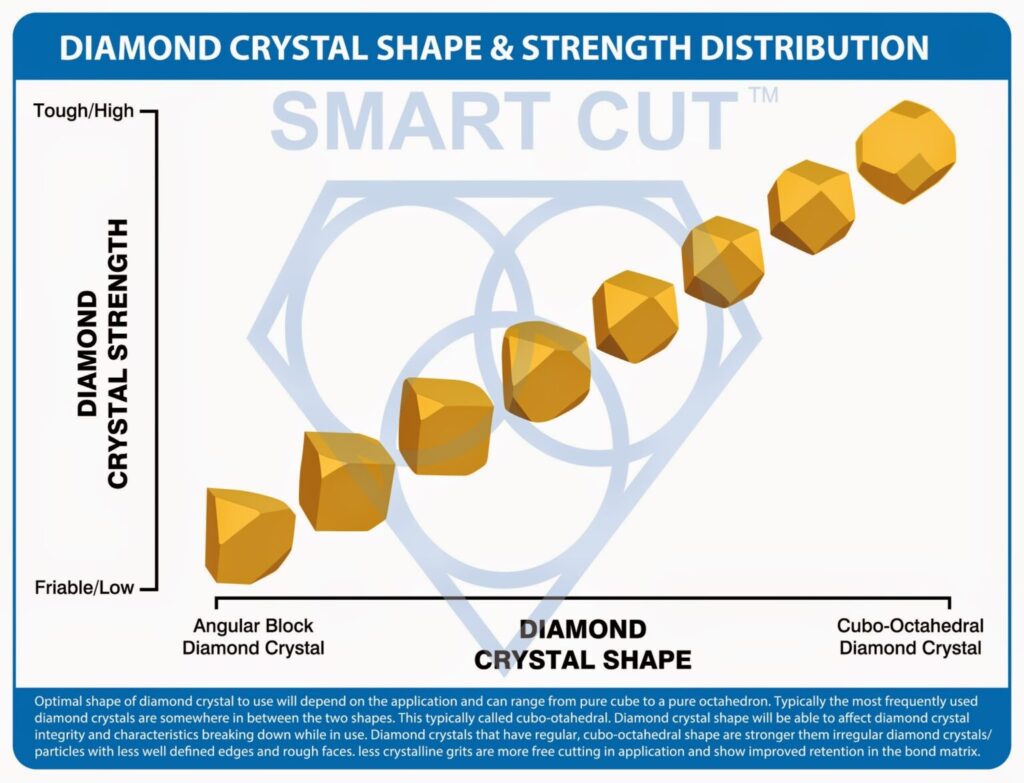
The ability of a diamond to withstand an impact load is typically referred to as diamond impact strength. Other diamond-related factors, such as crystal shape, size, inclusions and the distribution of these crystal properties, play a role in the impact strength as well. Impact strength can be measured and is commonly referred to as Toughness Index (TI). In addition, crystals are also subjected to very high temperatures during manufacturing and sometimes during the cutting process. Thermal Toughness Index (TTI) is the measure of the ability of a diamond crystal to withstand thermal cycling. Subjecting the diamond crystals to high temperature, allowing them to return to room temperature, and then measuring the change in toughness makes this measurement useful to a diamond tool manufacturer.

The manufacturer must select the right diamond based on previous experience or input from the operator in the field. This decision is based, in part, on the tool's design, bond properties, material to be cut and machine power. These factors must be balanced by the selection of diamond grade and concentration that will provide the operator with optimum performance at a suitable cost.
DIAMOND STRENGTH
An overly strong diamond crystal will either be broken or lost, but an overly wear diamond crystal will be disintegrated too fast. For this reason diamond crystal strength must be adjusted to suit the impart force in such a way that micro chipping is the dominant mode of wear and occurs more slowly
Diamond crystal wear mechanism is dependent on diamond strength. In order to optimize the cutting performance in both cutting ration and cutting speed, diamond crystal loss must be turned to micro chipping at the expensive of smashing and pullout/micro fracture

If a tough diamond crystal is used to cut hard material will either be broken or it will be knocked off the bond matrix, depending on bond matrix hardness in comparison to diamond crystal. IF a diamond that is friable is embedded in a cushion
like a resin bond matrix and used to cut very hard material. Friable diamond will provide best level of performance at smaller cutting depth.
With deeper cutting depth the diamond crystal will be smashed quickly, yet with smaller cutting depth this diamond will stay sharp by forming microchips gradually. In this matter the shaper diamond crystals can penetrate the hard material and cut it in most efficient mater, by utilizing electrical energy. Diamond friability will increase with increasing toughness of the material. Here is each diamond crystal can cover a certain range of toughness. Diamond crystal will develop a wear flat and become too dull to penetrate.


Find more information about diamond specifications>>>
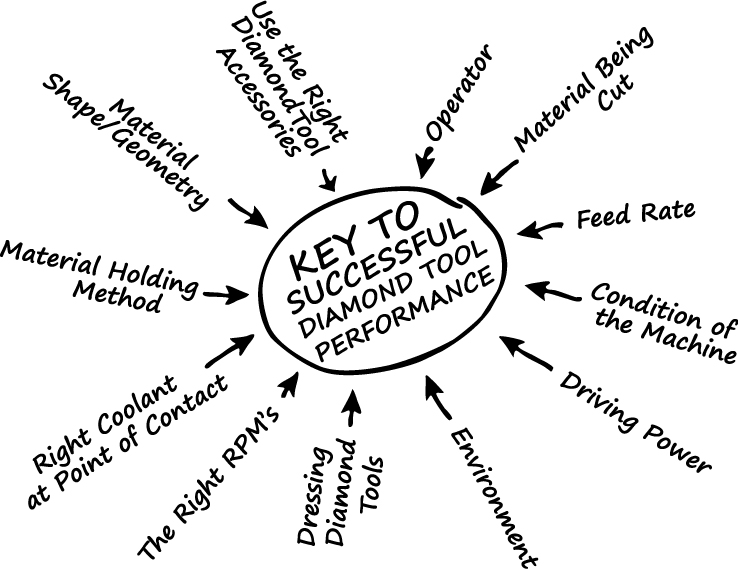
DIAMOND & CBN BLADE VARIABLES
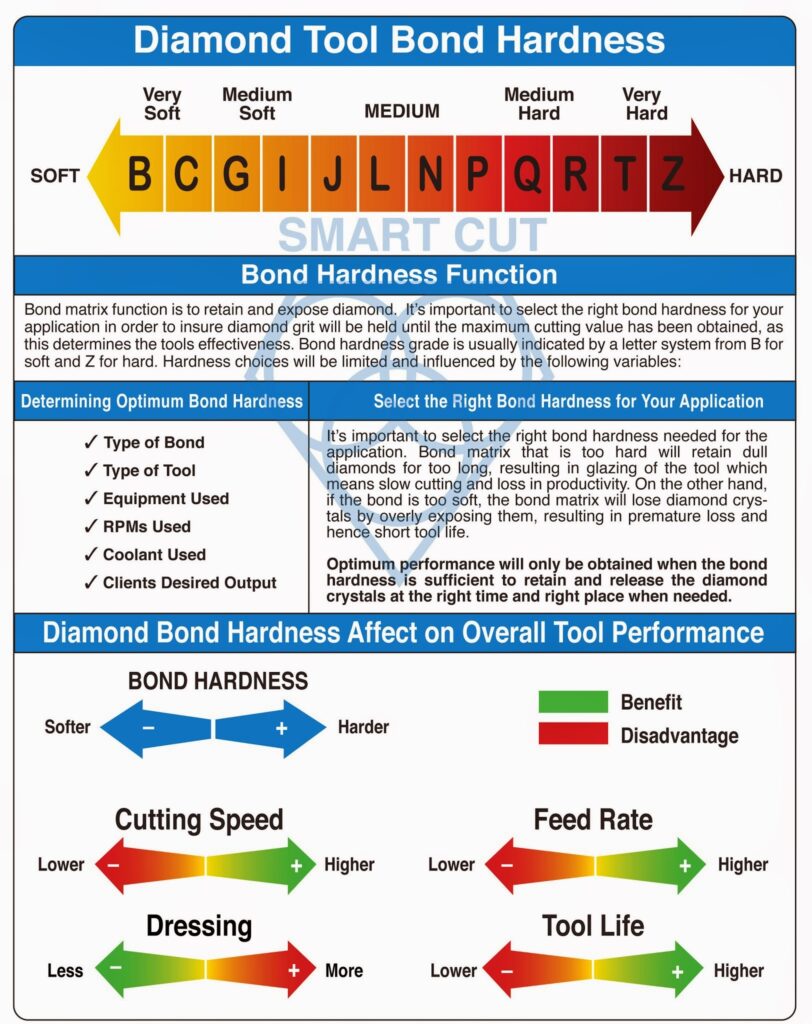
BOND HARDNESS

Bond matrix that is too soft for the material being cut will release diamond particles faster than needed, resulting in faster wear and shorter diamond blade life. On other hand bond matrix that is too hard will result in much slower cutting speeds and require constant dressing to expose the next diamond layer. As rule of thumb, harder materials such as sapphire and alumina generally require a softer bond. Whereas softer and more brittle materials require a harder bond.

Find more information about diamond bond hardness>>>
DIAMOND OR CBN DEPTH/HEIGHT

Diamond depth (height) indicates the Hight of diamond section/layer extends from the steel Core. Diamond depth will determine life of the blade. Higher the diamond height the longer. The blade life in most cases (depending on diamond concentration). Diamond height varies, depending on the bond type, diameter, and kerf thickness of the blade. Its size is determined by proportion of the blade diameter and thickness. For example very thin diamond blades cannot have very high diamond depth as the blade will be very fragile and prone to breakage. Usually there is correlation between diamond depth and price of the blade.
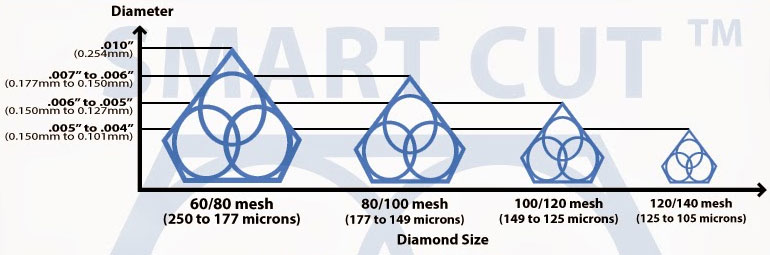
DIAMOND GRIT SIZE (Mesh Size)
grit size (mesh size) is generally selected depending on the speed you wish to operate the cut and surface finish of your material. According to U.S. Standards, mesh designates the approximate number of sieve meshes per inch. High Mesh Sizes mean fine grits, and low numbers indicate coarse grits. Diamond Mesh Size plays a major role in determining the surface finish quality, smoothness, level of chipping you will obtain, and material microstructure damage you will obtain.

Finer mesh size diamonds such as 220 and 320 grit are much smaller in size than coarser diamond particles. And will give you a very smooth surface finish, with minimal amount of chipping on edges. These mesh sizes are usually used for fine cutting of a full rage of materials such as: LiNbO3, YVO4, GaAs, and optical materials. Courser diamond particles such as 80 and 100 grit are much larger in diameter and are frequently used fast cutting / material removal on more harder materials such as silicon carbide, zirconia, Al2O3, stainless steels, and other advanced ceramics and high metallic content materials. Which do not require a very fine surface finish. A full range of diamond Mesh Sizes is utilized for precision diamond sawing operations ranging from as coarse as 60 mesh to as fine as 3 microns (5,000 mesh).

The diamond mesh size in a cutting tool also directly relates to the number of crystals per carat and the free cutting capability of the diamond tool. The smaller the mesh size, the larger the diamond crystals, while larger mesh size means smaller diamond. A 30/40 Mesh blocky diamond has about 660 crystals per carat, while a 40/50 Mesh diamond will have 1,700 crystals per carat. Specifying the proper mesh size is the job of the diamond wheel manufacturer. Producing the right number of cutting points can maximize the life of the tool and minimize the machine power requirements. As an example, a diamond tool manufacturer may choose to use a finer mesh size to increase the number of cutting crystals on a low concentration tool, which improves tool life and power requirements.

Diamond Mesh size does have considerable effect on cutting speed. Coarse Diamonds are larger than finer diamonds and will remove more material than finer diamond particles. This means that coarse diamond wheels are more aggressive for material removal than the finer diamond wheels and will cut faster. However, the tradeoff is increase in material micro damage. If you are cutting fragile, more delicate materials then finer mesh size diamond blades are recommended. Diamond mesh size (grit size) should provide maximum removal rate at minimal acceptable finish. Often the desired finish cannot be achieved in a single step/operation. Lapping or polishing may be necessary to produce desired surface finish, as a secondary step in your diamond sawing operation / process.

Recommended diamond mesh size will vary depending on blade type, bond, thickness, machinery used, industry, coolant used, industry, and many other factors

General diamond mesh sizes ranges are recommended and used for metal bond (sintered) 1A1R diamond cut off blades:
COARSE DIAMOND MESH SIZE – 20-60 is used for most masonry, refractory, concrete, and natural stone
MEDIUM DIAMOND MESH SIZE – 80-220 is used for most industrial materials such as glass, porcelain, ceramics, quartz, ultra hard & brittle materials and etc.\
FINE DIAMOND MESH SIZE – 240-400 is used for extremely smooth cutting, grinding and polishing.
If the letters S is included, it designates a mixture of diamond sizes is used in bond. By using a mixture of a coarse and fine diamond mesh sizes. The customer may be able to obtain benefit of fast cutting while maintaining a chip free, smooth cut.



Find more information about diamond mesh/grit size>>>
DIAMOND CONCENTRATION
The proportion, and distribution of diamond abrasive particles, also known as concentration. has an effect on overall cutting performance and price of precision diamond blades. Diamond concentration, commonly referred to as CON, is a measure of the amount of diamond contained in a diamond section of drill based upon volume.

Diamond concentration is usually defined as: Concentration 100 = 4.4 ct per cm layer volume (mesh size + bond). Based on this definition a concentration of 100 means that the diamond proportion is 25% by volume of diamond layer, assuming at diamond density is 3.52 g/cm3 and 1 ct = 0.2g. Nominal diamond concentration in precision diamond blades range from 0.5 ct/cm3 to 6 ct/cm3. This means diamond concentrations are available from 8 to 135). Selecting the Right Diamond Concentration can be critical in optimizing your Precision Diamond Sawing Operation. Selecting Optimum Diamond Concentration for your application

will depend on a large number of factors, such as

-
 Material Being Cut.
Material Being Cut.
-
 Bond Type and Hardness
Bond Type and Hardness
-
 Diamond Mesh Size
Diamond Mesh Size
-
 Cutting Speeds
Cutting Speeds
-
 Coolants being used
Coolants being used
Diamond Concentration will play a major role in determining the life and cutting speed of your High Precision Diamond Blade. Higher diamond concentration is recommended and usually used for cutting softer and more abrasive types of materials. However, the trade off is significantly slower cutting speed. Low diamond concentration is recommended and widely used for cutting ultra hard and brittle materials. Diamond Concentration is usually determined by the the slowest cutting speed that is acceptable for a specific application. Optimum performance can be achieved when the diamond tool manufacturer utilizes their experience and analytical capabilities to balance diamond concentration and other factors to achieve optimum performance for the tool operator. UKAM Industrial Superhard Tools has the experience & applications laboratory to help you select all the right diamond blade variables for your unique application.

Example of diamond concentration uses on various applications:
Diamond Concentration & Cutting Performance
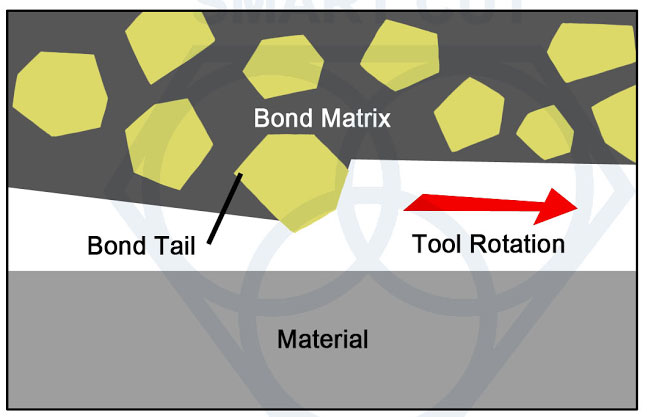
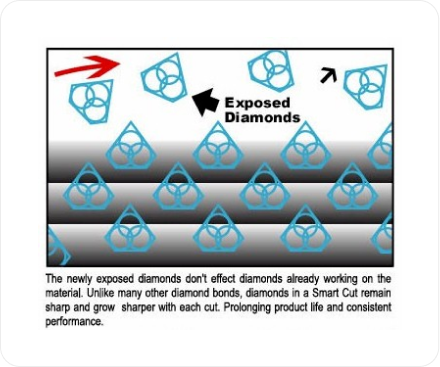
Today, most Production and R & D facilities use low concentration diamond blades for cutting ceramics, glasses, silicon, carbides, sapphire, and other related semiconductor and optical materials. And use high concentration diamond blades on metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, pc boards. A new technological breakthrough called SMART CUT™ technology, is making fundamental changes in these beliefs and setting new benchmarks on how diamond blade performance is measured. SMART CUT technology allows the orientation of diamonds inside the metal matrix, so that every diamond is better able to participate in cutting action, By orienting diamonds, SMART CUT™ technology makes diamond concentration only a minor factor in the overall precision diamond equation. Studies and extensive testing shows that diamond concentration in diamond blades manufactured utilizing SMART CUT™ technology plays a no major role in determining overall diamond blade performance.


Large number of diamonds in a high concentration diamond blade come in contact with material, creating friction, hence considerably slowing down material removal rate. It takes considerable dressing in order to rexpose the next diamond layer. SMART CUT™ technology resolves this problem by making sure that every diamond is in the right place and at the right time, working where you need it most. You get maximum use of diamond and bond. Before this technology was developed, orienting diamonds inside the blade bond matrix was considered impossible. This was one of the main problems faced by diamond tool manufacturers worldwide.
Over the decades there have been numerous attempts to solve the diamond and CBN distribution problem. Unfortunately, none of the attempts have been proven effective. Even today 99.8% diamond blade manufacturers still have no way or technology to evenly control and distribute Diamond or CBN particles inside bond matrix, nor properly position them to maximize their machining efficiency.
Diamond Concentration & CBN (cubic boron nitride) blades
Find more information about diamond concentration>>>
DIAMOND BLADE KERF THICKNESS
Typically thickness usually ranges from .004” (0.1mm) to .125” (3.2mm). Thinner and thicker kerf blades are also available. Kerf thickness typically increase with blade diameter (in proportion to diameter of the blade). Kerf is the amount Of material removed from the material due to the thickness of the blade passing through the material. Blade thickness is important for users requiring most minimal amount of material loss during cutting.
There are large variety of factors that will contribute to optimal blade thickness of your material & application Including your desired cutting speed, load/feed rate, material diameter, thickness, hardness, density and shape. As well as skill & experience of the operator. Thicker blade are more stiff and can take higher loads/fee rates. Another advantage of thicker kerf blades is they are more Forgiving to operator error and abuse. Thicker kerf blades are recommended for use in environment where Large number of individuals will be sharing and using same equipment, dry cutting, and less experiences operators
-
 less loss of material
less loss of material
-
 minimum material deformation / preserve true material micro structure
minimum material deformation / preserve true material micro structure
-
 less heat generation
less heat generation
-
 faster cutting speed
faster cutting speed
-
 less chipping
less chipping
-
 better finish quality
better finish quality
DIAMOND & CBN BLADE OUTSIDE DIAMETER
The diameter of the blade will depend on material thickness & cutting depth, rpm’s and specification of your cutting machine, and flange diameter. The blade should be large enough to clear through the material being cut. Also make sure to check the machine specification that it can accommodate the necessary blade diameter and provide the proper rmp’s range
DIAMOND & CBN BLADE INSIDE DIAMETER
Using a blade with right inside diameter to fit your cutting machine is important. We can machine the diameter of almost any blade to almost any inside diameter you require same day and also have many bushings in stock, as well as manufacture custom bushings. Bushings are used to reduce the blade inside diameter. We can also machine pin holes where needed.
DIAMOND & CBN BLADE Kerf cutting angle/radius
The blade's radius or angle, also known as the blade profile or rim type, can significantly impact the cutting performance and the quality of the finished cut. Various angles ground on the diamond edge can help improve cut quality, reduce chipping and provide particular slot/grove geometry.
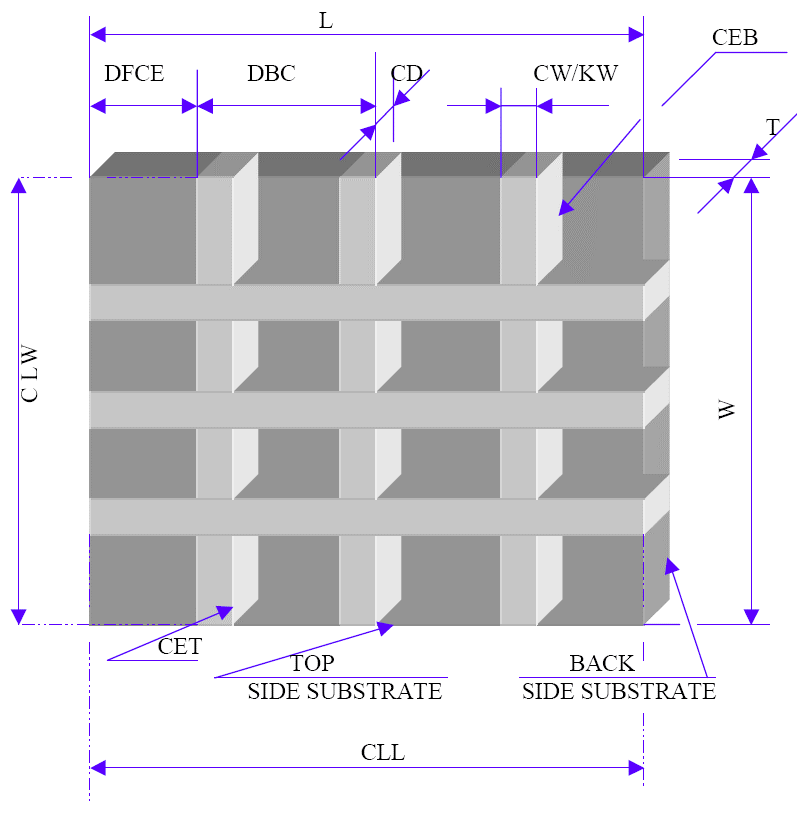
DIAMOND & CBN BLADES SLOTS / SEGMENTS
Segment Spacing Affect on Performance
Application Rules

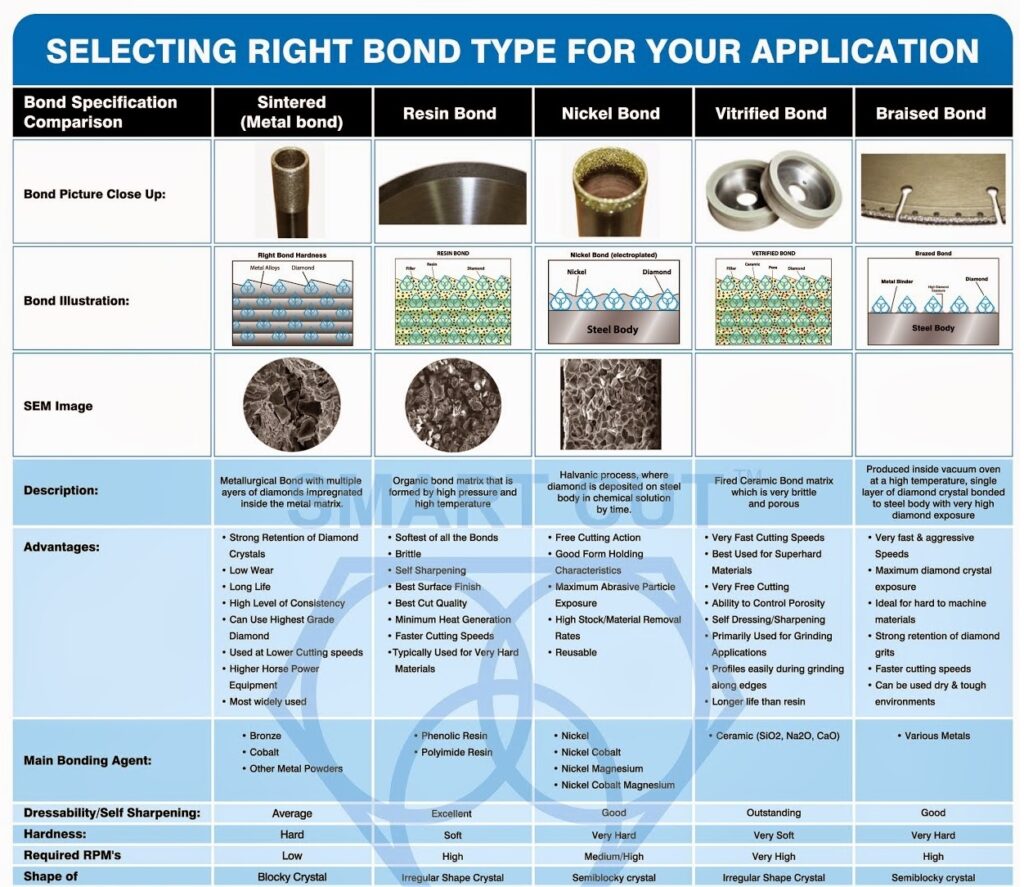
SELECTING RIGHT BLADE BOND TYPE FOR YOUR APPLICATION
WAFERING BLADE BOND TYPES
RESIN BOND
RESIN BOND SINTERED (METAL BOND)
NICKEL BOND



Bond Illustration



SEM Bond Cross Section






Applications
DIAMOND, Resin Bond
-
 Alumina
Alumina
-
 Barium Titanate
Barium Titanate
-
 Garenet
Garenet
-
 Glass & Quartz
Glass & Quartz
-
 Ferrite
Ferrite
-
 LiNb03
LiNb03
-
 Silicon
Silicon
-
 Fused Silica
Fused Silica
-
 Electronic Ceramics
Electronic Ceramics
-
 Sapphire
Sapphire
-
 Ultra Hard & Brittle Materials
Ultra Hard & Brittle Materials
-
 Sapphire
Sapphire
-
 Carbon Fiber Tubing
Carbon Fiber Tubing
-
 Silicon Nitride
Silicon Nitride
-
 Rare Earth Magentic Materials
Rare Earth Magentic Materials
-
 Zirconia
Zirconia
CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride)
-
 Moybedum
Moybedum
-
 Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten Carbide
-
 Ferrites
Ferrites
-
 Cast Iron
Cast Iron
-
 HSS Punches
HSS Punches
-
 HSS Hardened
HSS Hardened
-
 Ni Hard Rods
Ni Hard Rods
-
 Titanium
Titanium
-
 Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel
-
 High Alloy Steel
High Alloy Steel
-
 Chrome Nickel
Chrome Nickel
-
 Superalloys Hardened Tool Steels
Superalloys Hardened Tool Steels
DIAMOND, Sintered (metal bond)
-
 FR4/BT Resin
FR4/BT Resin
-
 Alumina
Alumina
-
 Glass
Glass
-
 Copper & PCB
Copper & PCB
-
 AITIC
AITIC
-
 Green Ceramic
Green Ceramic
-
 Plastic Laminates
Plastic Laminates
-
 Zirconia
Zirconia
-
 Rare Earth Magnets
Rare Earth Magnets
-
 Fired Multi Layered Ceramics
Fired Multi Layered Ceramics
-
 copper
copper
-
 aluminum
aluminum
-
 metal matrix composites
metal matrix composites
-
 pc boards
pc boards
-
 thermal spray coatings
thermal spray coatings
-
 titanium alloys
titanium alloys
-
 glass
glass
-
 Al203
Al203
-
 Zr203
Zr203
-
 Concrete
Concrete
-
 soft ceramics
soft ceramics
-
 electronic packages
electronic packages
-
 integrated circuits
integrated circuits
-
 GaAs
GaAs
-
 Glass
Glass
-
 Stone
Stone
-
 Aslphalt
Aslphalt
CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride)
-
 carbon steels
carbon steels
-
 high speed steel
high speed steel
-
 tool steels
tool steels
-
 alloy steels
alloy steels
-
 hardening steels
hardening steels
-
 die steels
die steels
-
 stainless steels
stainless steels
-
 bearing steels
bearing steels
-
 Heat Resistant Alloys
Heat Resistant Alloys
-
 Sintered Metals
Sintered Metals
-
 Copper Alloys.
Copper Alloys.
-
 Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum Alloys
-
 Cast Iron
Cast Iron
-
 Tugsten
Tugsten
-
 Flame Sprayed Metals
Flame Sprayed Metals
-
 Magentic Materials
Magentic Materials
DIAMOND, (nickel bond)
-
 Fiber reinforced composites
Fiber reinforced composites
-
 Plastics
Plastics
-
 Graphite
Graphite
-
 Fiberglass
Fiberglass
-
 Epoxy
Epoxy
-
 Silicon
Silicon
-
 Bones
Bones
-
 GRP
GRP
-
 pre-sintered and pre- fired (green) materials
pre-sintered and pre- fired (green) materials
-
 thermosetting plastics
thermosetting plastics
-
 electro carbons
electro carbons
-
 soft ferrites
soft ferrites
-
 farinaceous products
farinaceous products
-
 deep frozen fish
deep frozen fish
-
 pones
pones
-
 Resins
Resins
-
 Acrylic
Acrylic
-
 glass fibers
glass fibers
-
 composites
composites
CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride)
-
 tool and die steels,
tool and die steels,
-
 high alloy steels,
high alloy steels,
-
 nickel rich alloys.
nickel rich alloys.
-
 soft metals
soft metals
-
 Meteorites
Meteorites
-
 rubber
rubber
-
 plastics
plastics
-
 Very soft & Gummy Materials
Very soft & Gummy Materials
Bond Characteristics
superior cut quality than the finest size metal bond (sintered)
bade. Recommended for cutting hard, brittle or delicate materials including ceramics, carbides, composites and exotic metals where low heat generation or improved surface finish
is desired.
multiple layers of diamonds impregnated inside the metal matrix Provide longer then resin bond and nickel bond blades. They wear evenly, and are known fortheir long life & consistency. Used in vast majority of cutting applications.
have a single layer of diamonds, held by a tough durable nickel alloy. diamond particles to protrude from the bond matrix, providing a free, faster cutting action with minimum heat generation
Adventages
-
 Unmatched Cut Quality
Unmatched Cut Quality
-
 Free Cutting & Self Sharpening
Free Cutting & Self Sharpening
-
 Faster & Freer Cutting Speed
Faster & Freer Cutting Speed
-
 Less Heat Generation than
Less Heat Generation than
-
 Less Stress to material
Less Stress to material
-
 Will cut the hardest material
Will cut the hardest material
-
 Can be used dry (without coolant) when needed
Can be used dry (without coolant) when needed
-
 Can withstand Higher Temperature
Can withstand Higher Temperature
-
 Perfect for fragile and delicate materials
Perfect for fragile and delicate materials
-
 Perfect for cutting tubing materials with no chipping
Perfect for cutting tubing materials with no chipping
-
 More Universal, used on majority of applications
More Universal, used on majority of applications
-
 Longer Life than other bond types
Longer Life than other bond types
-
 Largest Range of Specifications available from stock
Largest Range of Specifications available from stock
-
 Preserve True material Micro Structure
Preserve True material Micro Structure
-
 Freer and faster cutting action
Freer and faster cutting action
-
 High Diamond Exposure
High Diamond Exposure
-
 Thinnest possible kerfs available
Thinnest possible kerfs available
-
 More forgiving to operator errors
More forgiving to operator errors
-
 Lower Cost
Lower Cost
-
 May be used without coolant (on some
May be used without coolant (on some
-
 Does not Gum up on soft materials such as plastics & composites applications)*
Does not Gum up on soft materials such as plastics & composites applications)*
Core Type
High carbon steel
Bronze (non magnetic)
High carbon steel
Memory Steel Stainless Steel
Alloy
(Diamond/CBN) Sizes Avaialble
80 to 320 mesh
50 to 400 mesh
50 to 320 mesh
Diamond Depth (height)
5mm, 6.4mm
4mm, 7mm, 10mm, fully sintered
1/16", 1/8"
Diamond Concentration
25 to 200 con
25 to 200 con
100 to 250 con
Minimum Blade Thickness
.015" (.381mm)
.006" (0.101mm)
.007" (0.0076mm)
Coolant Used
Can be used with synthetic water soluble coolant or mineral oil. can be used without coolant in many applications when needed
Must be used with synthetic water soluble coolant or mineral oil, or water at minimum.Cannot be used without coolant in over 95% of applications
Can be used with synthetic water soluble coolant or mineral oil or water. can be used without coolant in many applications when needed
Blade Life
Medium
Longest
Longest
Minimum RPM's
50
1,000
450
SELECTING THE RIGHT DIAMOND & CBN BLADE & BOND FOR YOUR APPLICATION
M = Sintered (Metal Bond). R = Resin Bond. H = Hybrid Bond. E = Electroplated (Nickel Bond. MCBN = Metal Bond Cubic Boron Nitride. RCBN = Resin Bond Cubic Boron Nitride. HCBN = Hybrid Bond Cubic Boron Nitride
Acrylic Glass
Agate
Al-Ni-Co
Alumina (fused)
Aramit Fibre Plastics
Barium Titanate
Boron Carbide
BrakeLining
Cemented Carbide
CERAMICS
Oxide ceramics, sintered
Al2O3 (aluminium oxide)
Al2O3(tubes)
Al2O3 (electronic resistors)
Al2O3 (seals)
CarbideCeramics
TIC (titanium carbide)
NITRIDE CERAMICS
Si3N4 (HPSN) silicon nitride
Ceramic Tiles
Ceramics Unfired
Chrome Nickel (10% Cr, 90% Ni)
CRP (carbon reinforced plastic)
Epoxy Resin Boards
Epoxy Copper-Clad with circuits
Eternite (asbestos-free)
Formica (nameplates)
Germanium (semiconductor)
GGG (semiconductor)
GlassOptical
Glass Fibres (bundeled)
GlassSheet
GlassCeramics
Glass Hard Laminate (cast epoxy)
Glass Fibre Reinforced
Glass Laminates (safety/bullet proof glass)
Glass (quartz glass tubes)
GlassWool
Glass(pyrostop)
Glass (thick optics)
Glass Technical
Glass Fibre Rod
Glass Hard Laminate
Granite
Graphite
GRP (window sections)
GRP (constructional sections)
E
M
RCBN
M
M
R/H
M
M
M/R
M
R/H
E/M
M
R/H
M
E
RCBN/HCBN
M
E
E/M
M
E/R/H
M
E/R
M
E
E
M/H
R/H
E
M/H
M/H
M
E
R/H
M
E/M
E
M
M/H
R/H
E
M/H
M/H
M
E
R/H
GRP (internal thermoplastic ring)
Helopal Panels (plastic)
Hematite
HSS Punches
HSS Hardened
Insulators Ceramic
Lapis Lazuli
MAGNETIC MATERIALS
Ferrites Sintered
Ferrites Cast
Rare Earth Magnetic Materials
Samarium Cobalt
Malachite
Marble
MelamineResin
Metal Coated Ceramics
Moybdenum
Mycalex (cast stone)
Ni Hard Rods
Piezoceramics
Polycarbonate (glass reinforced)
PolystyreneSheets Printed CircuitBoards
PVCHard
Quartz (fusable)
Quartz (synthetic)
Rhodochrosite
Rose Quartz
Sapphire
Sendust
Sendust
Silicon
Silicon Carbide (pressed & crushed) Silicon(monocrystalline) (polycrystalline
Silicon (semiconductor)
SiliconNitride
Silicon Carbide (ReSiC)
Steatite
Stellite
Tiger’sEye
Titanium
TitaniumCarbide
TitaniumZirconate
Topaz
Tungsten
Tungsten Wires
UraniumDioxide
Uranium
Zirconium
E
E
M
RCBN
RCBN
M
M
M/R
MCBN
R/H
M/R
M
M/E
E
E/M
RCBN/H
M/E
RCBN
M
E
E
E/M
E/M
M/R
M
M
M
M/R/H
E
E
M
M
M
R/H
R/H
M/R/MCBN
M
M
M/R/H
M
M
M
M/R/E
M
M
M
M
Diamond Blades & Cutting Speeds
The RPM’s of the machine spindle should be noted when selecting the right blade specification of your application. So that the blade will be tensioned to run at the operating speed. This will insure a true running blade. Adherence to recommended speed is very important. Improper blade speeds can be rectified in many cases with a pulley change or change in blade diameter. Blade specification can be modified to some degree is speed is not correct, however deviation from recommended SFM should be amended for maximum performance. Make sure the cutting machine you are using is designed or can be adapter to be used for your application. Many machines are designed for other diamond blade applications and may not be ideal for you to use.
Ultra Thin & High Precison Diamond Blades can be used either at low or high speeds. There are advantages and disadvantages of each process. Diamond may break (fracture) at very high speeds, and fall out at very slow speeds. An optimum surface speed / RPM's must be selected to balance out the two disadvantages. Diamond Blade life will usually increase at slower cutting speeds. However the increase in labor costs, utilities costs, depreciation of equipment and other overhead expenses. Will usually offset the saving of diamond blade life and other consumables. Cutting Speed & Surface Finish Quality is often the most important consideration when selecting the right diamond blade for your application. The operator mush choose a balance between life of the blades and their cutting rate. Diamond has a higher impact strength than the material being machined. During the sawing operation, the diamond ruptures the material by impact. Each diamond is able to transfer the electrical power from your cutting machine, into momentum that breaks the material on nano / micro level.
By increasing power on your saw, your diamond blade RPM's and surface speed will increase as well. Hence, each diamond will chip off a smaller amount of material, reducing its impact force on material being machined. And reducing cutting resistance. In theory, by increasing surface speed / RPM's, each diamond should receive a smaller impact force. However, because impact is supported by a smaller volume, the impact force with this low volume is actually increased. There is a higher probability that the diamond particles will break or shatter. Hence, cutting materials at very low surface speeds, creates a large impact force between diamond and material being machined. Although the diamond may not break, the risk that the diamond will be pulled out of diamond blade and causing premature failure of the blade increases.
Understanding Material Hardness & its affect on Diamond Blade Performance
Material Hardness has several meanings. Most common definition for material hardness refers to its ability to resist deformation. Scientifically hardness is defined by energy density (energy per unit volume) required to create strain in material. While there are many ways, scales, and classification schemes to measure material hardness. In this article we will address the most simple explanation.
Mohs scale of Abrasion Hardness is the most simple and well known material hardness measurement and classification methods. In this scale material hardness is measured by scratch test of rubbing each material against another. All material harnesses are arranged in 10 ranks. Each rank is calibrated by a standard mineral. Below find these minerals in their rank of hardness from softest to hardest.
Diamond is the hardest material known to mankind. It can penetrate into any material. Brittle or Soft materials such as granite, advanced ceramics, and copper can be cut by diamond, without diamond particles being broken or exhibiting large pull out. However, when cutting very tough and dense materials such as cemented/tungsten carbide, the contact pressure of each diamond particle must be increased in order to allow diamond to penetrate being cut. The Hardness, Density, & Brittleness of the material being cut will determine whether the diamonds inside the diamond bond matrix need to be blocky and tough enough in order to break (rupture) material by brutal force or if they should be friable & flexible to penetrate the material by sharp points.

Mohs Scale of Hardness
1 Gypsum
2 Calcite
3 Fluorite
4 Apatite
5 Orthoclase
6 Quartz
7 Topaz
8 Corundum
10 Diamond
Hierarchy
Rank
Examples
Ultrasoft
< 5
graphite, salt, talc, lead, teflon
Soft
5-8
silver, copper, calcite, fluorite
Normal
8-10
magnesia, glass, steel, quartz
Hard
10-12
WC, SiC, Al203, Si3N4, B4C
Superhard
> 12
cubic boron nitride, Diamond
Proposed Scale of Hardness for Industrial Materials
Hierarchy
Formula
Mohs Hardness
Knoop Hardness
Rank
Industrial Hardness
Graphite
C
1 -
12
3.6
3
Molybdenite
MoS2
1
17
4.1
4
Aluminum, annealed
Al
2 -
25
4.6
Table Salt
NaCl
2
30
4.9
Gypsum
CaSo4
2
32
5.0
5
Silver
Ag
2 +
60
5.9
6
Mild Steel, annealed
Fe
2 +
123
6.9
Calcite
CaCO3
3
135
7.1
7
Copper
Cu
4
163
7.3
Indium Antimonide
InSB
4+
220
7.8
8
Magnesia
MgO
5-
370
8.5
Glass
Soda lime
6-
530
9.0
9
Tool Steel
Fe
6+
700
9.5
Quartz
SiO2
7
820
9.7
Chromium
Cr
7
935
9
Zirconia
ZrO2
8-
1160
10.2
10
Cemented WC
WC-Co(8%)
8-
1200
10.2
Beryllia
BeO
8-
1250
10.3
Silicon
Se
8-
1400
10.5
Titanium nitride
TiN
9-
1800
10.8
Corundum
Al203
9
2100
11
11
Silicon Nitride
Si3N4
9
2100
11
Tungsten Carbide
WC
9+
2400
11.2
Titanium Carbide
TiC
9+
2470
11.3
Silicon Carbide
SiC
9+
2480
11.5
Boron Carbide
B4C
9+
3000
11.6
Sintered cBN
BN
10-
3200
11.6
Cubic boron nitride
BN
10-
4800
12.2
12
Sintered diamond
C
10-
5000
12.3
Diamond (Type IIa)
C
10
9000
13.1
13
Evaluating Diamond Blade Performance
The performance of a diamond blade for just about any application / material can be evaluated under various criteria. The importance of any criteria depends on your requirements.
Cutting Life - The life of a diamond blade is determined by the number of cuts it can make. It is fairly difficult to estimate the life of diamond cut. Diamond blade life is affected by various factors such as the application, bond type, blade manufacturer, and experience of user in properly using the blade. The following considerations play a major role in diamond blade life:
-
 hardness and abrasiveness of the material being cut
hardness and abrasiveness of the material being cut
-
 RPM's (speed) and power of your equipment
RPM's (speed) and power of your equipment
-
 amount of pressure used (feed rate)
amount of pressure used (feed rate)
-
 proper use of coolant (type of coolant, coolant force, & direction)
proper use of coolant (type of coolant, coolant force, & direction)
-
 operator experience (Understanding Proper Diamond Blade Usage Principals and adjusting them as need to better fit their particular application & objectives)
operator experience (Understanding Proper Diamond Blade Usage Principals and adjusting them as need to better fit their particular application & objectives)
-
 overall age and condition of cutting equipment (precision, accuracy, & repeatability of cutting equipment. As well as Flange Diameter & Maintenance condition of equipment used)
overall age and condition of cutting equipment (precision, accuracy, & repeatability of cutting equipment. As well as Flange Diameter & Maintenance condition of equipment used)
-
 mesh size of the diamonds
mesh size of the diamonds
-
 hardness of the bond compared to the material being cut
hardness of the bond compared to the material being cut
-
 experience and technology of manufacturer in keeping diamonds in the bond
experience and technology of manufacturer in keeping diamonds in the bond
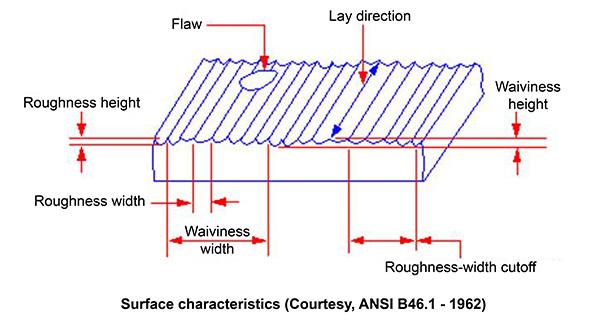
Surface Finish Quality - The quality of the surface finish is evaluated by the amount of chips generated on the face of the material. Surface finish consists of three basic components: form, waviness and roughness. Although there are more then 100 ways to measure a surface and analyze results. A visual check is the most simple & easiest way of measuring (checking) surface finish quality. The most common scientific way of measuring surface finish quality is using Ra, or Arithmetic Average Roughness. It basically reflects the average height of roughness component irregularities from a mean line. Ra provides a simple value for accept/reject decisions.
Break in time - A diamond blade requires time to break in, to produce relatively chip free performance. The period of time under which this occurs, separates one diamond blade from another.
Frequency of Dressing - The less you have to dress your diamond blade, the better off you will be.
A diamond blade is fundamentally a cutting tool consisting of bond and diamonds. Diamonds are the cutting tool and bond is the medium by which the system is regulated. In purchasing diamond blades, many customers are often concerned about diamond concentration as a dominant factor in pre determining a diamond blades basic value. Diamond concentration may be an important consideration in
performance of diamond blades – but it is essential to understand the concentration is not by any means the sole criterion of diamond blade evaluation.
Each diamond blade manufacturer has its own standard for relating diamond concentration to diamond content. In evaluating a diamond blades potential value to you it is important to take into account a variety of cutting variables – only one of which may be diamond content.
Diamond blade cost is usually a minor factor in the grand picture. Whereas labor and overhead costs are more important factors in the total cost picture. Therefore it is important to select a diamond blade that can provide the most performance and productivity, not the lowest blade cost. This product should not be purchased on the basis of price or concentration only, but on the basis of cost per piece cut. Cost performance evaluation is your insurance policy protecting you against taking account of less than all of the variables.
Understanding Diamond Blade Bond Types & their Application
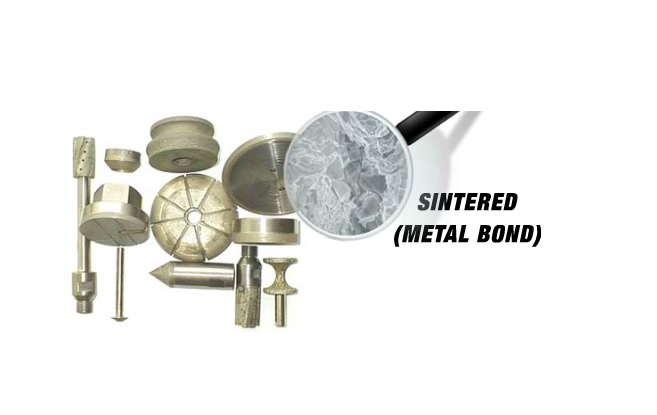
SINTERED (MEAL BOND) DIAMOND & CBN BLADES












Sintered (Metal bonded) diamond blades diamonds sintered and multiple layers of diamonds impregnated inside the metal matrix. Diamonds are furnaces sintered in a matrix made of iron, cobalt, nickel, bronze, copper, tungsten, alloys of these powders or other metals in various combinations. Metal Bonded Diamond Tools are “impregnated” with diamonds. The compacted materials are then hot pressed or sintered to full density. Heating rate, applied pressure, sintering temperature and holding time, are all controlled according to the matrix composition.
This means that selected diamonds are mixed and sintered with specific metal alloys to achieve the best cutting performance possible on any materials such as sapphire, advanced ceramics, optics, glass, granite, tile and etc. The metal bond surrounding the diamonds must wear away todiamond blades longer than other diamond bond blades such as resin bond and electroplated (nickel bond) blades. They wear evenly, and are known for their long life & consistency. Sintered (metal bonded) diamond blades are the latest technology available in Diamond Blades. And represent the best value and performance per cut. Metal bond matrix does not protrude diamonds very high and hence usually requires lower cutting speeds than electroplated (nickel bond) and resin bond blades. continuously keep re-exposing the diamonds for the diamond tool to continue cutting. Sintered (metal bonded) diamond tools are recommended for machining hard materials from 45 to 75 on Rockwell Scale (5 to 9.5 on mohs scale of hardness). It is more wear resistant and holds diamond well in place, usually producing the highest yield/cutting ratio. As a general rule of thumb, Metal Bond (sintered)
The letter M designates metal as the type bonding used. Through research in metal powder metallurgy, metal bond has become the most universal bonding material for diamond products. No other bonding utilizes so well the extreme durability of diamonds as an abrasive. It is possible to vary and control the toughness of metal to a great degree while maintaining maximum blade life.
SINTERED METAL BOND TYPES
This is perhaps the most important factor in selecting the right diamond blade specification for your application/material. The proper metal bond will hold the diamond particles to their full cutting capability, after which they will be released so that new diamonds can take their place. Diamond blades must have a wear factor. The proper wear factor will provide maximum blade life while remaining sharp, fast and smooth cutting. The bond grading indicates the relative strength or holding powder of the bond.

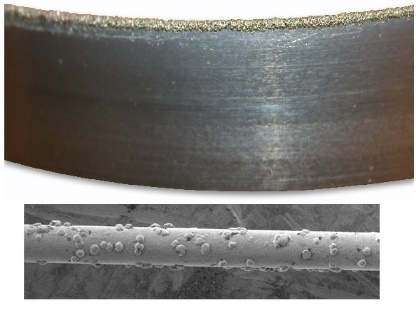
SEM Image of Sintered (metal bond) diamond cut off blade
Examples of most common sintered (metal bonds) used for cutting application
B BOND – a friable bond recommended for very hard materials such as quartz, ferrite, hard ceramics, and glass. It will yield the fastest, smoothest cut
M Bond– The general purpose bond for industry. This bond will offer a longer blade life than the A bond when used on the same materials
C Bond– A very tough bond for abrasive and soft materials such as carbon, graphite, plastics and fiber glass
Find more information about sintered (metal bond) blades>>>
RESIN BOND DIAMOND & CBN BLADES






Resin Bond Diamond Blades last less than Sintered (Metal Bond) diamond blades, but more than electroplated (nickel bond) diamond blades. Resin Bond is the softest of all the bonds, frequently used in applications that require a smooth surface finish and minimum amount of chipping. Made from a tough polymer formed to hold the diamond particles in the bond. A resin bond is really tar in a solid form. A resin bond must remain very fragile in order to expose new diamonds. For this reason, strong and high quality diamonds cannot be used in a resin bond.
High quality diamonds are harder than a resin bond matrix, and would soon disintegrate the bond that keeps them in place. The diamonds that are used in a resin bond are poor to medium quality. Most of them prematurely disintegrate or fall out of the bond, before they have a chance of being used. This brings about the need for frequent blade dressing, causing the cut to loose its roundness or form. Another disadvantage of Resin bond is its high wear rate, lack of stiffness, and thickness limitation. Resin bond can cut hard & brittle materials fast, but will provide much shorter life. Thinnest blades that can be produced in resin bond is .004". A more durable bond is sintered (metal

Find more information about resin bond blades>>><./span>
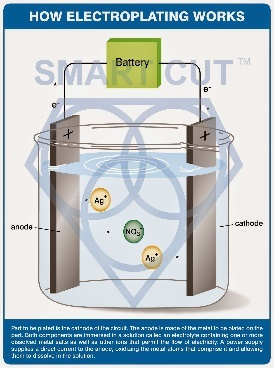
ELECTROPLATED (NICKEL BOND) DIAMOND & CBN BLADES











Find more information about nickel bond (plated) blades>>>
Electroplated Diamond Blades have a high diamond concentration and give a freer, faster cutting action with minimum heat generation. Diamonds stay on the surface of the cut allowing for fast material removal. Electroplated Diamond Blades last less than metal bond, resin bond, hybrid bond blades and are the least expensive diamond blades available. Perfect for smaller jobs and beginning cutting operations. Just about the only type of diamond blade that may be used dry (without coolant) in a few applications, excellent for cutting very soft, ductile, & gummy materials. Electroplated diamond blades are frequently used for dry cutting (when coolant cannot be used). Electroplated blades a particularly well suited for cutting thermosetting plastics, GRP, pre-sintered and pre-fired (green) materials, electro carbons, graphite, soft ferrites, farinaceous products, deep frozen fish, bones, pc boards, and etc.

Braised Bond Diamond & CBN Blades








Brazed Diamond Blades are produced using and process that creates a fusion between the diamonds and the metal bond. While they may appear similar to electroplated (nickel bond) diamond tools. They are produced utilizing completely different process. Brazed Bond Diamond Tools are produced inside vacuum oven at a high temperature, single layer of diamond crystal bonded to steel body with very high diamond exposure.
Not only does it promote high diamond exposure, but it also eliminates the loss of diamond particles through pull-out. The diamond section will not strip or peel from the steel body. This translates into multiple benefits, including: aggressive tools that last longer, cut faster, run cooler and load less, providing increased productivity and part consistency.
Find more information about braised bond blades>>>
HYBRID BOND Diamond & CBN Blades




Introducing the HYBRID BOND, a breakthrough solution developed in direct response to customer demand for Reduced Wear Resin Bond Tools. In 2006, after extensive Research & Development and rigorous testing, we successfully created a revolutionary bond that surpasses the limitations of traditional resin bond diamond tools.
HYBRID BOND Tools exhibit exceptional longevity, maintaining superior form, shape, and extended lifespan while consistently delivering outstanding performance.
These tools are designed to expand the application of tooling, overcoming the limitations of conventional resin bond diamond tools. You can now experience the advantages of cutting speed and improved surface finish that you have come to expect from resin bond, coupled with the durability, consistency, aggressiveness, and excellent performance typically associated with sintered (metal bond) tools.
Resin-bonded diamond & CBN tools have long been recognized for their fast material removal. However, the majority of resin bond diamond tools suffer from rapid wear and require frequent dressing (truing) to maintain their shape. In contrast, our HYBRID BOND offers a stronger bond type comparable to sintered (metal bond) tools. It provides longer tool life and better retention of form, enabling operation at higher speeds.
While sintered (metal bond) diamond tools are known for their edge quality and surface finish, many users have found them unsuitable for their specific applications. This limitation no longer exists with our HYBRID BOND. It bridges the gap between resin bond and sintered (metal bond), offering edge quality, surface finish, and the performance you desire.
Find more information about hybrid bond blades>>>
Abrasive Cut Off Blades



Abrasive cut-off blades work based on the principle of abrasive cutting, where a rotating disk with abrasive particles embedded in it cuts through the material by grinding away its surface. These blades are typically composed of a circular steel disk with abrasive grains distributed throughout its surface. The abrasive particles can be made of materials like silicon carbide or diamond, depending on the hardness of the material to be cut.
Abrasive cut-off blades are efficient in cutting a wide range of materials, from metals and ceramics to composites and plastics.
Find more information about abrasive cut off blades>>>
Carbide Blades


fine teeth tungsten Carbide blades are available from 3” (75mm) to 8” (200mm) OD, thickneness from from .004” (100 microns). Standard arbor is ½”, but can be made any size. Ttypically used on low speed cutting machine. Typical application are materials where diamond cannot be effective used such as green ceramics, PC Board substrates, fiberglass, laminates, MLP/QFN, soft and gummy materials and similar applications.will be made from special type of metal to minimize dust and corrosion. Come with ultra precise chucks, collets, water pumps and devices. With these types of drill press you are usually able to regulate drilling depth either electronically or by computer, maintain consistent speed and feed rate. More advanced drill presses today may have feed back mechanism that provides information on all of these variables.
Find more information about carbide blades>>>